Leather is a material rich in history and valued for its strength, texture, and how it can be styled into truly timeless fashion, furniture, and utility items. Be it the men’s leather jacket or great sophisticated leather bags, acquiring proper knowledge about leather can help you decide to buy for or even be an enthusiast.
Dive into the info spring to find out the different types of leather, shedding the lid off questions like what the types of leather are, explaining which leather type and its uses, and comparing full-grain vs. top-grain leather. The end will answer what defines high-quality leather from the rest and how to select the best fit for you.
Introduction to Leather Types
Leather is a very broad term with no single definition. It’s not one product that can be stereotyped as uniform, but rather a varied quality, texture, and finish. It results from different animal hides used to make the leather, different types of tanning and finishing processes followed, and what kind of final use or application the leather is to have. This flexibility helps leather serve an array of industries ranging from fashion, furniture, and automotive to accessories.
At its very basic level, leather comes in two broad categories: Natural Leather and Synthetic Leather. These groups have different properties, applications, and appeals. Let’s break them down further.
Natural Leather Types
Natural leather is an animal hide that has been specially treated and processed to make it into tough, usable material. The species of the hide, such as cowhide, sheep skin, or even crocodile or snake skin, is one factor that will define what properties are in the leather. Natural leathers enjoy the truthfulness of the authenticity, strengths, and unique textures of these products.
Cowhide Leather
It is one of the strongest leather types and is resistant to wear and tear. Cowhide leather is good for heavy-duty items like men’s leather jackets, shoes, belts, wallets, furniture, and luggage. Opt for a full-grain or top-grain cowhide for long-lasting products.
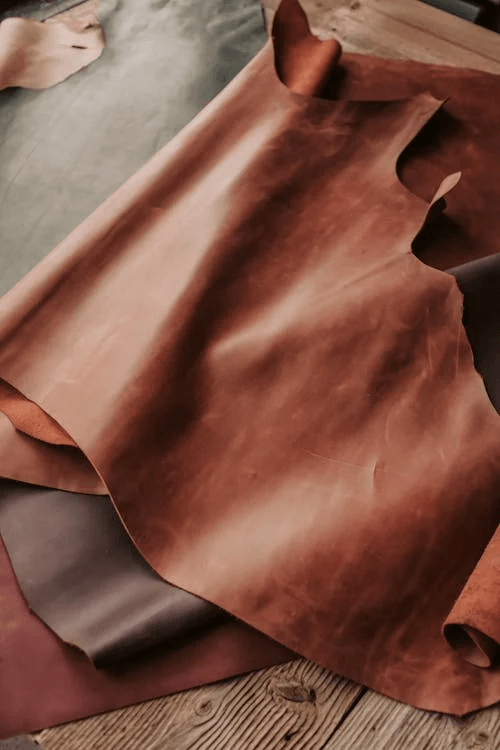

Sheepskin Leather
Sheepskin leather is softer and more pliable than cowhide. They are lightweight, breathable, slightly warmer, and perfect for layered clothing, garments, women’s leather jackets, gloves, and accessories.

Goat Leather
Goat leather strikes a balance between durability and flexibility and is often used in accessories, traditional bags, boots, gloves, and outerwear. It is naturally grainy with a slightly oily finish.

Lambskin Leather
Often mistaken for sheep skin, lambskin leather is fine and soft, with a luxurious feel, lambskin leather is barely durable enough for high-end fashion skirts, handbags, and sophisticated leather bags—thin in texture and very light.

Calfskin Leather
Calfskin leather refers to the superior leather with a smooth surface and fine grain. Such leather is very much in demand due to its flexibility and softness. It retains durability while being softer than cowhide. Commonly used to craft high-end shoes, wallets, and briefcases.

Exotic Leathers
Exotic leather comes from non-traditional sources of animals, such as crocodiles and snakes—giving unique scales used in handbags and wallets, and Ostrich hides for a dimpled texture known for durability. Commonly used in watch straps, belts, and luxury accessories.

Natural leather has an extraordinary aging quality, which is sometimes sealed with a patina that changes with the years, giving uniqueness to the material. This, however, also needs care and maintenance for it to remain of good quality.
Why Understanding Leather Types Matters
The differences between real leather and genuine leather, or what is full-grain leather compared to what is faux leather, may seem subtle, but they have profound implications for durability, style, and cost.
Synthetic Leather
Contrasted to this, synthetic leather is an artificial material that is almost identical in terms of look and feel to the real article. It’s commonly referred to as faux leather and is crafted from a variety of synthetic polymers like polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC). While it doesn’t have the same longevity or authenticity as natural leather, synthetic leather offers several advantages.

Ethical Appeal
Faux leather is non-animal, so it also appeals to any consumer wishing for less animal damage or vegan alternatives.
Cost-Effective
Synthetic leather is comparatively more affordable than its natural counterpart and, hence, more accessible.
Versatility
Versatility can be made in a variety of textures and finishing preferences, such as matt, gloss, and distressed, and in colors. Therefore, it can be applied to things like upholstery, footwear, and fashion accessories.
However, synthetic leather does not age like natural leather. It does not pick up patina but, instead, tends to degrade with time, getting cracked or peeled. In spite of that, its lower cost, ethical considerations, and other considerations make it a tough competition in the leather market.
Synthetic Leather: Pros and Cons
What is faux leather? Faux leather is an artificial alternative that resembles the appearance of natural leather. Even though it comes with its benefits, it surely has several drawbacks.
Advantages of Faux Leather
- Affordable: more affordable than authentic leather and, therefore, affordable for budget-conscious consumers.
- Vegan-Friendly: No animal products, appealing to ethical consumers.
- Versatile Designs: Available in a range of textures, finishes, and colors.
Disadvantages of Faux Leather
- Durability: Lacks the longevity of natural leather.
- Aging: Tends to crack or peel over time, unlike natural leather that ages gracefully.
Faux leather pros and cons are worth considering when buying items like upholstery, jackets, or bags.
Specialty Leathers and Their Unique Characteristics
Some types of leather are subjected to additional finishing processes in order to enhance their visual and functional attributes. Here are a few specialty leathers described:
Full-Grain Leather
Full-grain leather is the highest quality leather, featuring the complete grain of the hide. Its natural imperfections give it character. Full-grain leather is extremely durable and develops a patina over time. Often used to craft luxury furniture, boots, and belts.
Top-Grain Leather
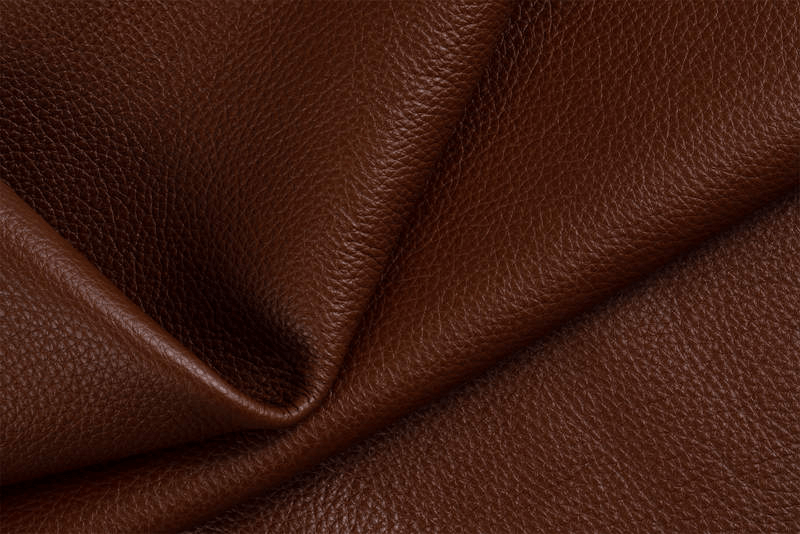

Second only to full-grain, top-grain leather features a sanded surface for a more uniform look, slightly less strong than full-grain. Commonly used to craft high-end jackets, bags, and wallets. However, top-grain vs. full-grain remains a key consideration for those prioritizing durability over aesthetics.
Genuine Leather
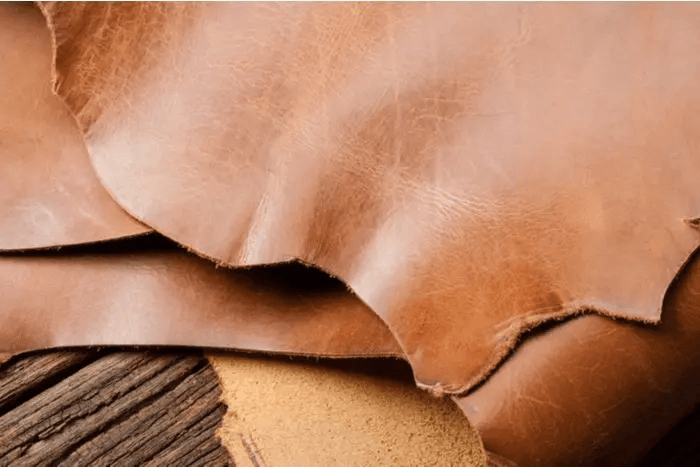

Contrary to its name genuine leather, it’s a lower grade made from leftover hide layers, quite decent for casual use but less durable. It is perfect for producing budget-friendly belts and shoes.
Split Leather
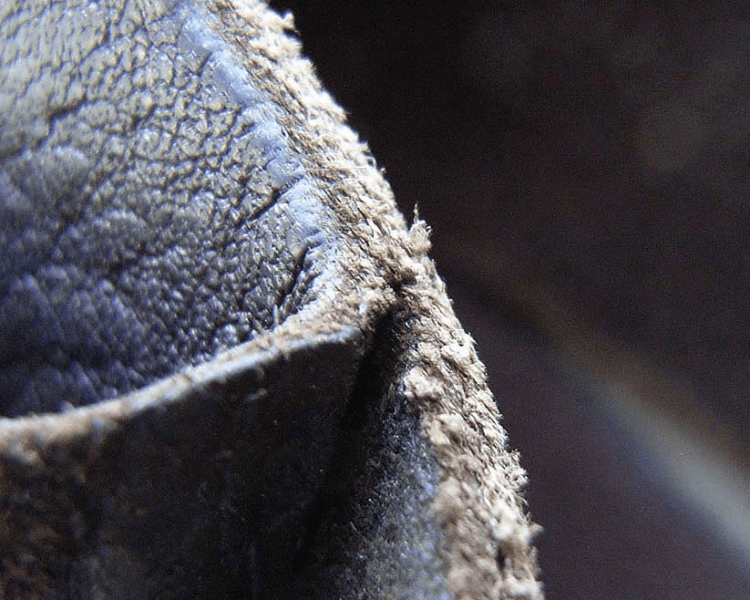

Split leather is crafted from the lower layer of the animal hide and is often coated for durability. Nubuck and suede leather can be categorized as split leather, commonly indulged in crafting upholstery, gloves, and shoes.
Nubuck Leather
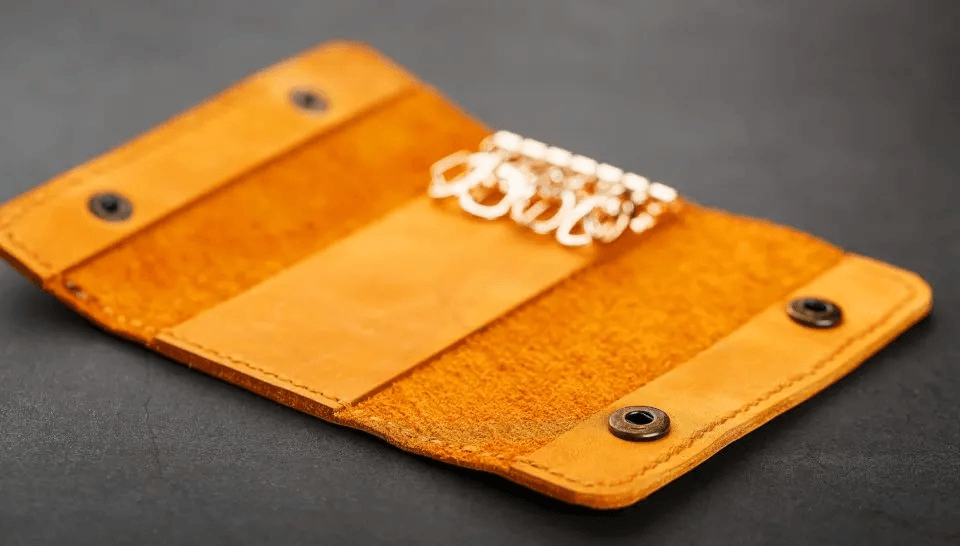

Nubuck leather is created by sanding the grain side of the hide for a velvety feel. It has a soft yet durable texture. Shoes, bags, and jackets are crafted from nubuck leather.
Suede Leather
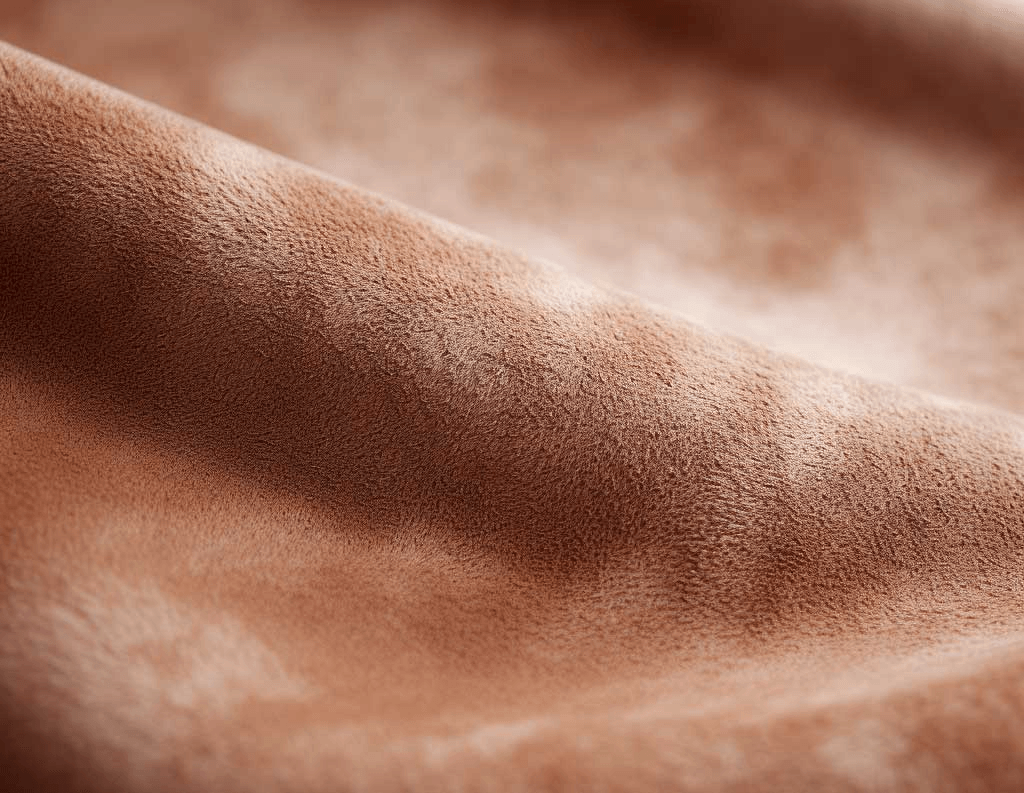

This leather is made from the underside of the hide. That is, the suede leather finish is softer than others, lightweight, and stylish. Commonly used in jackets, boots, and handbags.
Pigmented Leather
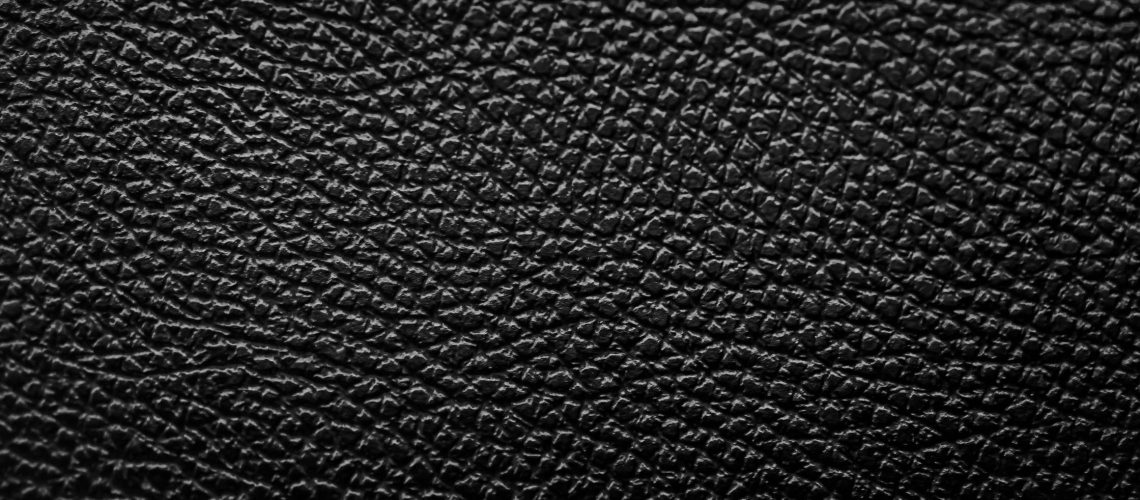

What is pigmented leather? This leather employs pigments. Coating of these pigments provides this leather with uniform coloring along with enhanced strength—perfect for automotive interiors and sofas.
Aniline and Semi-Aniline Leather

What is aniline leather? — It’s dyed without coatings, maintaining the hide’s natural look. Likewise, semi-aniline leather has a light protective coating for stain resistance and is commonly used in furniture and luxury goods.
Leather Tanning Methods
Tanning transforms raw hides into usable leather. The method impacts the leather’s quality and appearance.
Vegetable Tanning
This is an eco-friendly method that uses natural tannins, such as those coming from plants such as tree bark and leaves. It is quite time-consuming, but the leather produced this way is strong and unique. Vegetable-tanned leather gains a beautiful patina with time, so when aging, it will look even better. It is firm and perfectly appropriate for structured items such as a belt, wallet, and bag. It is not water-resistant, so it is better used as an accessory rather than for heavy-duty use outdoors.
Chrome Tanning
Chrome tanning is a quick, flexible process widely used for mass production. Its dependence on chromium salts means that hides can be processed within a day. Leather produced using this process will be soft, supple, and in a wide range of colors, thus suitable for jackets, shoes, and other furniture. However, this leather type is less environmentally friendly but highly durable and supple, and it is used on products that require the aspect of flexibility and comfort.
Combination Tanning
Combination tanning merges vegetable and chrome tanning, offering the best of both methods. It creates leather that is soft and flexible, like chrome-tanned leather, but also durable and able to develop a patina like vegetable-tanned leather. A very common hybrid is used for items that necessitate a combination of strength and elegance, such as high-quality footwear, bags, or garments.
Comparing Leather Finishes
The finish of the leather dictates the final look and feel. Some common leather finishes are the following:
Distressed Leather
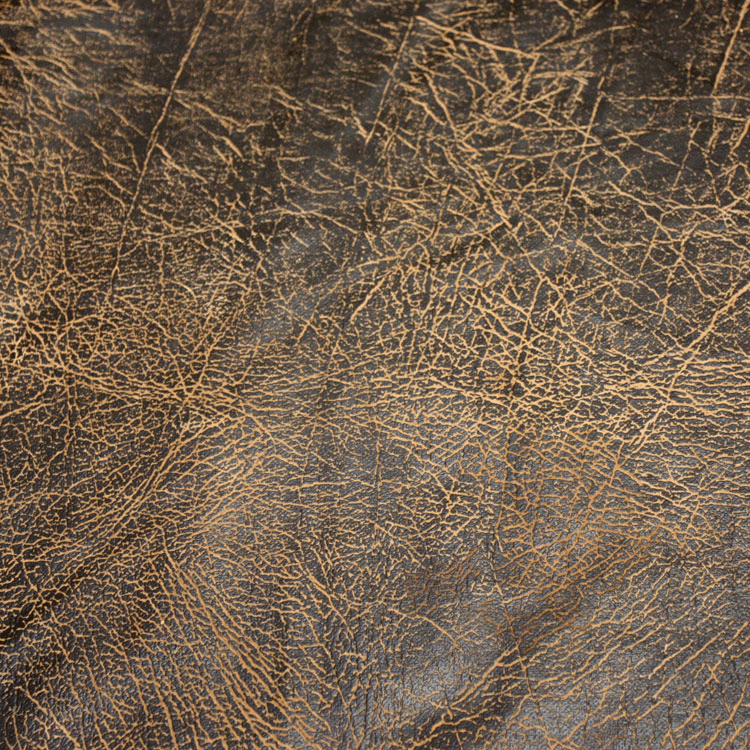

Distressed leather has gained immense popularity in the past few years among those who have a rugged, vintage look requirement because its style resembles the wear and tear that develops with time. This makes it an ideal choice for casual jackets and boots, giving them a rather effortless, lived-in look.
Patent Leather
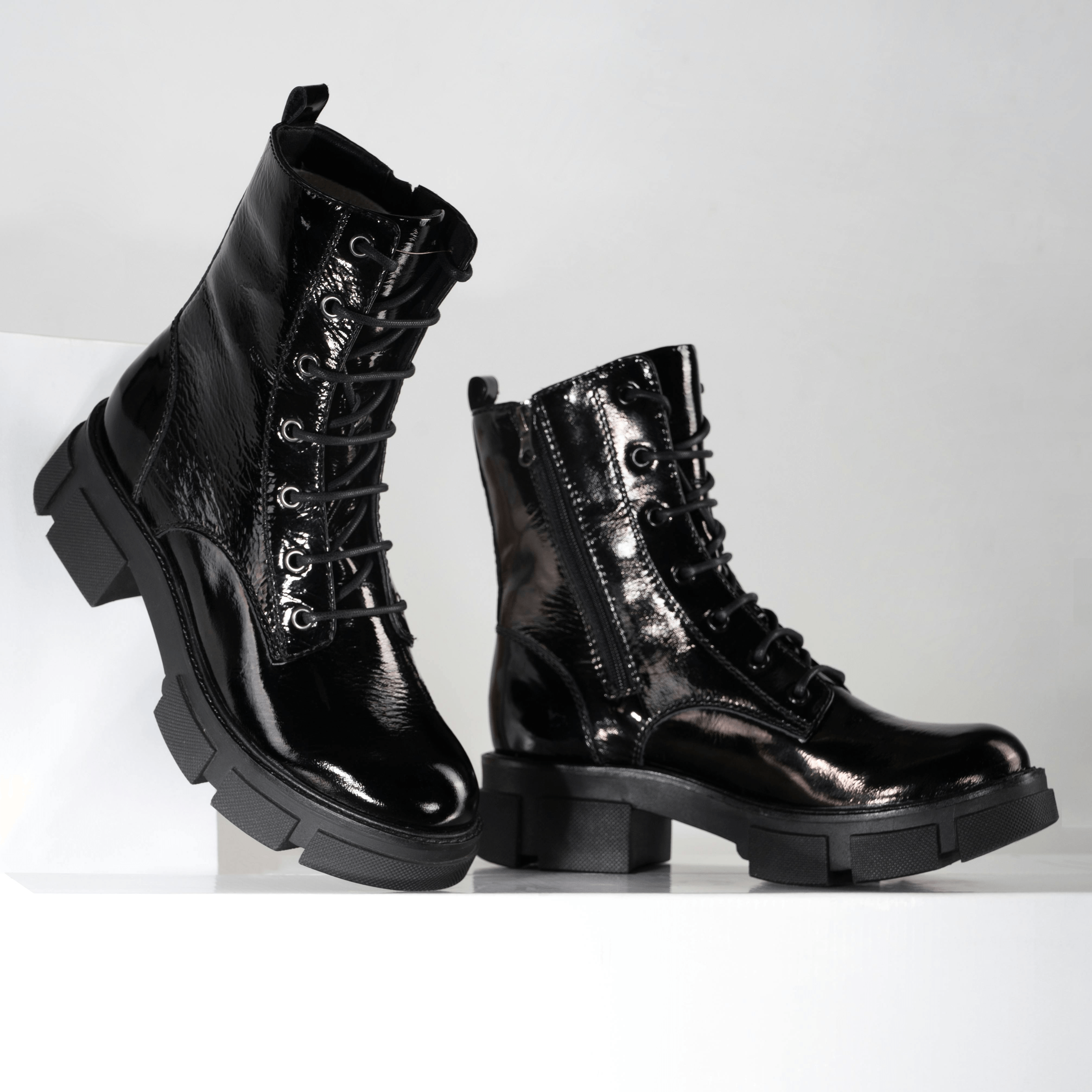

Patent leather is commonly acknowledged for its high-gloss finish with a very good sheen that appears reflective. They can be used for shoes, handbags, and tuxedos at weddings, adding sophistication and polish.
Matte and Glossy Finishes
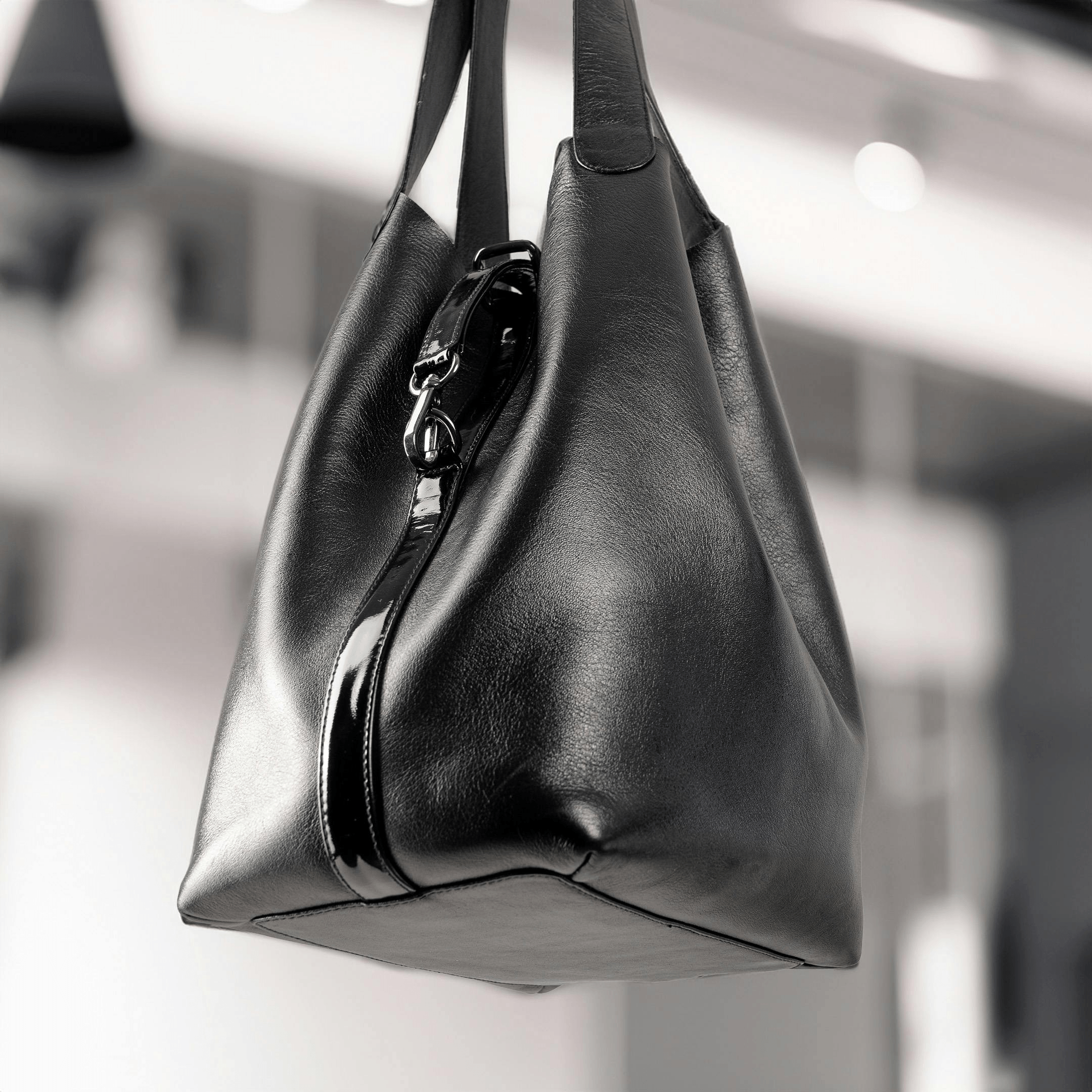

Matte leathers are understatedly elegant, while glossy finishes make a bold and attention-grabbing statement.
Pull-Up Leather
Another special leather is pull-up leather. When this type of leather is stretched, it darkens. This creates a dynamic, character-rich appearance that works especially well in jackets and bags.

Each of these finishes and types brings about their unique flair and functionality to different applications for clothing and accessories.
Conclusion
Knowing the types of leather allows one to appreciate this time-honored material. From selecting a suede leather jacket to deciding between top-grain and full-grain or trying to figure out what genuine leather is, matching characteristics with the needs of a piece can be done. You will know what to choose for a stylish yet resilient fashion future once you are acquainted with the difference between real leather and faux leather. Leather, after all, remains an element of quality and sophistication, no matter how it evolved.





Thanks for sharing this best stuff with us!
Really all these types of leather backpacks are very nice. I like these types of backpacks. your article is very good.
This is a very interesting post. I haven’t read this type of article before. This information is very helpful and useful for me.
Excellent article. Still trying to understand pros and cons of sheep vs. goat skin for a jacket. I’ve spent 30+ hours trying to compare the two. Prefer smooth over brushed look. Looking for 3-season: Spring, Summer, Autumn.